The Soup Nut serves his signature minestrone soup in two different bowl sizes, large and small. What strategy should he use to extract the most surplus possible out of customers who come in two types, regular and big eaters, when he cannot distinguish between the two types by observation?
a. Distort the size of the small bowl downward to make it less attractive to the big eaters, allowing him to
raise the price of the large bowl.
b. Distort the size of the large bowl downward to make it attractive to both big and regular eaters.
c. Distort the size of the small bowl upward to make it harder for regular eaters to separate themselves from big eaters.
d. Distort the size of the large bowl upward to make big eaters less likely to consume the small bowl.
a
You might also like to view...
Policymakers focus on marginal tax rate changes when making changes in the tax code because the marginal tax rate
A) determines how tax revenue will change as national income increases. B) determines how much revenue the government will have to spend. C) always equals the average tax rate which is harder to measure. D) affects people's willingness to work, save, and invest.
Currently, total government expenditures in the United States have totaled about:
a. one-tenth of GDP. b. one-fifth of GDP. c. 40 percent of GDP. d. one-half of GDP.
Exhibit 10-2 A monopolistic competitive firm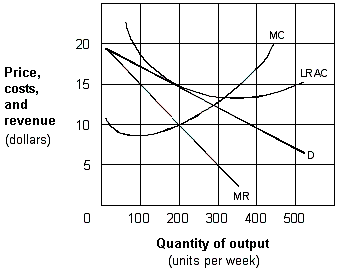
A. choose a price equal to the marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity. B. will experience entry of new firms into the industry. C. earn zero economic profits. D. minimize cost per unit at their profit-maximizing quantity.
If the perfect competitor is making a profit, its output will be ____ it's most efficient output.
A. more than B. equal to C. less than