Normative economics
A. answers the question "What is?"
B. predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
C. answers the question "What ought to be?"
D. is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph for a market to answer the question below.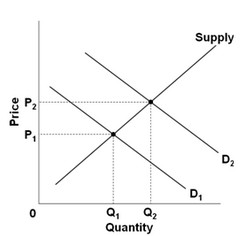 Which of the following could not explain the indicated increase in equilibrium price from P1 to P2?
Which of the following could not explain the indicated increase in equilibrium price from P1 to P2?
A. an increase in production costs B. an increase in consumer incomes C. an increase in the price of a substitute product D. a decrease in the price of a complementary product
When a firm's long-run average cost is constant as output increases, the firm is experiencing constant returns to scale
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Suppose a manager is deciding whether or not to purchase a piece of equipment to make an input internally and has completed the majority of the net present value (NPV) calculations. The manager has correctly calculated the NPV to be equal to: NPV = ($1.023 × Q) - $350,000, where Q is the annual quantity of the input the firm needs. If the firm needs 355,000 units of the input each year, the
manager ________ buy the equipment because the NPV is ________. A) should not; negative B) should; negative C) should not; positive D) should; positive
When a person wants to buy a used car, asymmetric information may land her with a “lemon” because:
a. neither she nor the dealer can know everything about the car. b. a used car is in a lower-risk category for insurance purposes. c. a used car that has been in an undisclosed accident could have alignment problems. d. the car dealer knows more about the car than she does.