Explain, using two examples, how continuing enhancements in technology can result in delivery of products and services both faster and better.
What will be an ideal response?
Answers will vary. Topics addressed might include: ability of apps and the Internet to allow faster and more accurate ordering, engineering, and communications with customer; presence of on-line forums and reviews to encourage product/service providers to improve their performance; ability of new technologies (e.g., robotics and 3-D printing) to manufacture products at less cost, with greater precision, more safely, and more consistently; etc.
You might also like to view...
Zymosis Manufacturing produces a pesticide chemical and uses process costing. There are three processing departments—Mixing, Refining, and Packaging. On January 1, the Refining Department had 2000 gallons of partially processed product in production. During January, 33,000 gallons were transferred in from the Mixing Department, and 29,000 gallons were completed and transferred out. At the end of the month, there were 6000 gallons of partially processed product remaining in the Refining Department. See additional details below.
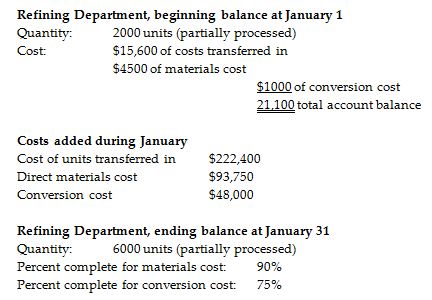
What was the cost per equivalent unit with respect to conversion costs for the Refining Department in the month of January? (Use the weighted-average method, and round your calculations to the nearest cent.)
A) $1.42
B) $1.46
C) $1.40
D) $8.17
In a breakeven graph, the slope the total cost line is dependent on the variable costs per unit
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Disparate impact is (are)
a. intentional discrimination against a protected group of persons, such as blacks or women. b. practices, which have unintentional discriminatory effect on a class of people, protected under Title VII. c. programs that attempt to "make up" for past patterns of discrimination. d. workers giving up the right to sue in court for on-the-job injuries.
Trane Medical Clinic offers a number of specialized medical services. A review of data for the year just ended revealed variable costs of $32 per patient day; annual fixed costs of $480,000, which are incurred evenly throughout the year; and semivariable costs that displayed the following behavior at the "peak" and "valley" of activity: January (2,400 patient days): $258,400August (2,900 patient days): $278,900Required: A. Calculate the total cost for an upcoming month (2,800 patient days) if current cost behavior patterns continue. Trane uses the high-low method to analyze cost behavior.B. There is a high probability that Trane's volume will increase in forthcoming months as patients take advantage of new scientific advances. Can the data and methodology used in part (a) for predicting
the costs of 2,800 patient days be employed to estimate the costs for, say, 3,800 patient days? Why or why not? What will be an ideal response?