An alloy of 80 atomic % arsenic and 20 atomic % gallium is produced, and the alloy is heated to 1250°C to thoroughly melt the mixture. The alloy is then slowly cooled so that it is always close to equilibrium. Answer the following about the alloy:
(a) At what temperature does a solid first form?
(b) What is the chemical composition of the first solid to form?
(c) Below what temperature is the alloy completely solid?
(d) At room temperature (23°C), what phases are present, what are their chemical compositions, and what is the atom fraction of each phase present?
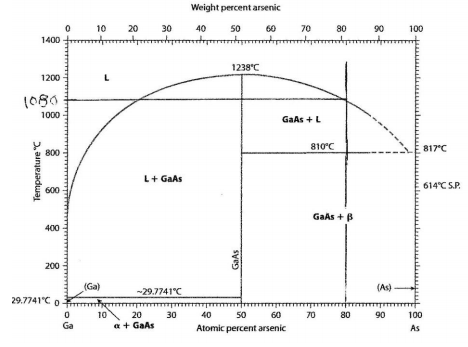
(a) The 80 atomic % arsenic line intersects the liquidus line at approximately 1080°C, this is the temperature where solid first starts to form upon cooling.
(b) The first solid to form is found by drawing a horizontal line at 1080°C, and this intersects the GaAs compound line at 50 atomic % arsenic. The first solid to form is GaAs with the chemical composition of 50 atomic % arsenic.
(c) Below 810°C this alloy is all solid, it is a mixture of solid beta and the compound GaAs.
(d) At 23°C there is the beta phase that is pure arsenic and the gamma phase has the chemical composition of 50 atomic % arsenic and 50 atomic % gallium. This is a two phase region thus the atom fraction of beta and gamma are given by the lever rule.
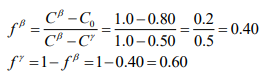
You might also like to view...
What does not happen when an object approaches a black hole?
A: it becomes redder because photons lose energy B: time runs more slowly as it gets closer to the black hole C: it quickly gets sucked in even from a large distance D: it gets stretched out because of tidal forces E: none of the above
The number of states in the He+ ion corresponding to the principle quantum number n = 5 are
a. 18 b. 25 c. 50 d. 9 e. 11
List the three useful ways in physics to multiply vectors
What will be an ideal response?
A 0.0030-kg lead bullet is traveling at a speed of 300 m/s when it embeds in a block of ice at 0°C. If all the heat generated goes into melting ice, what quantity of ice is melted? (Lf = 80 kcal/kg, the specific heat of lead = 0.03 kcal/kg•°C, and 1 kcal = 4186 J)
a. 1.47 × 10^-2 kg c. 3.2 × 10^-3 kg b. 4.0 × 10^-4 kg d. 2.6 × 10^-4 kg