Find the output voltage of the peak detector shown in Figure P9.66. Use sinusoidal input voltages with amplitude 6, 1.5, and 0.4 V. Let V? = 0.7 V.
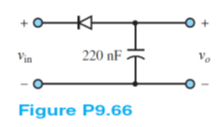
Analysis:
The capacitor will charge to .
6 V:
Therefore, the input sine wave will be shifted up 5.3 V to produce the output. As a result, after the cycle (the capacitor builds up its stored charge during the third quarter cycle), the average value of the output will be 5.3 V.
1.5 V:
Therefore, the input sine wave will be shifted up 0.8 V to produce the output. As a result, after the cycle (the capacitor builds up its stored charge during the third quarter cycle), the average value of the output will be 0.8 V.
0.4 V:
Since the input is less than 0.7 V, the capacitor does not charge and the output voltage is 0 V.
You might also like to view...
All of the following are considered job factors that impact the productivity of excavation and backfilling operations EXCEPT ________.
A. type of material excavated or backfilled B. access to or around site C. project size and complexity D. quality of job labor
Which of the following best describes the role of an air compressor?
A. a motor B. an engine C. an air pump D. an air cleaner
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of work cells?
A) Queue and lead time are reduced. B) Need for floor space is reduced. C) Immediate feedback D) Production activity control is simplified. E) Maximum machine utilization
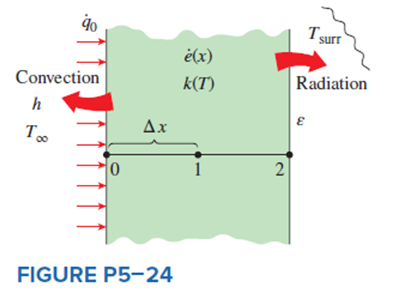
Consider steady one-dimensional heat conduction in a plane wall with variable heat generation and variable thermal conductivity. The nodal network of the medium consists of nodes 0, 1, and 2 with a uniform nodal spacing of ?x. Using the energy balance approach, obtain the finite difference formulation of this problem for the case of specified heat flux to the wall and convection at the left boundary (node 0) with a convection coefficient of h and ambient temperature of T?, and radiation at the right boundary (node 2) with an emissivity of ? and surrounding surface temperature of Tsurr.