Consider steady one-dimensional heat conduction in a plane wall with variable heat generation and variable thermal conductivity. The nodal network of the medium consists of nodes 0, 1, and 2 with a uniform nodal spacing of ?x. Using the energy balance approach, obtain the finite difference formulation of this problem for the case of specified heat flux to the wall and convection at the left boundary (node 0) with a convection coefficient of h and ambient temperature of T?, and radiation at the right boundary (node 2) with an emissivity of ? and surrounding surface temperature of Tsurr.
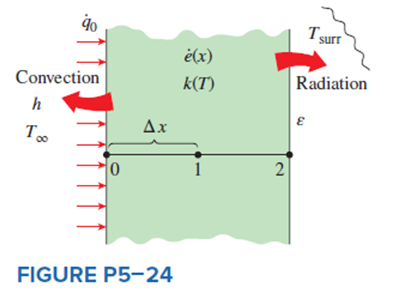
A plane wall with variable heat generation and variable thermal conductivity is subjected to specified heat flux and convection at the left boundary (node 0) and radiation at the right boundary (node 5). The complete finite difference formulation of this problem is to be obtained.
Assumptions 1 Heat transfer through the wall is given to be steady and one-dimensional, and the thermal conductivity and heat generation to be variable. 2 Convection heat transfer at the right surface is negligible.
Analysis Using the energy balance approach and taking the direction of all heat transfers to be towards the node under consideration, the finite difference formulations become
Node 0 (at left boundary):
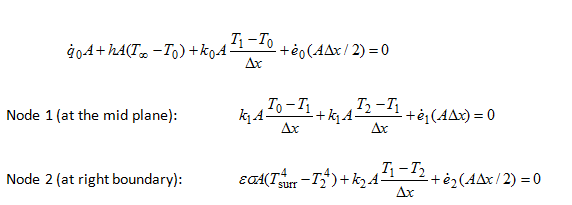
You might also like to view...
Dynamic braking can easily be demonstrated by applying direct current to an AC induction motor and turning the ____.
a. motor shaft by hand b. operator knob, not pushing it c. switch to the off position d. transistor on and off several times
Sometimes plants are named for where they grow naturally
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
What happens to the temperature of freshly cut forage when it is packed?
What will be an ideal response?
Block diagrams of PLC controlled systems are ________
A) Complex systems that are represented by a series of simple rectangles B) Provided by the equipment vendor C) Diagrams with information and signal flow from right to left D) All of the above