A stars exhibit strong hydrogen absorption lines because the surface temperature of 10,000 K is high enough to place most hydrogen in an excited, but not yet ionized, state
The transitions from this excited state then correspond to visible light wavelengths. Which of the following statements is a plausible explanation for why G stars exhibit weak hydrogen absorption lines?
A) G stars contain very little hydrogen.
B) At these high temperatures, nearly all the hydrogen is ionized, and unable to interact with light.
C) G stars are too cool to excite hydrogen atoms to the first energy level from which they can then absorb visible wavelengths of light.
C
You might also like to view...
When a ferromagnetic material that has been magnetized is brought to a temperature greater than the Curie temperature, what happens to its residual magnetism?
A. Nothing happens to the residual magnetism. B. The residual magnetism disappears. C. The residual magnetism reaches it's highest value. D. All the magnetic domains causing magnetism become a single domain. E. The material of the magnet melts causing currents that are magnetic.
Refer to the accompanying data set and use the 25 home voltage measurements to construct a frequency distribution with five classes. Begin with a lower class limit of 122.0 ?volts, and use a class width of 0.2 volt.
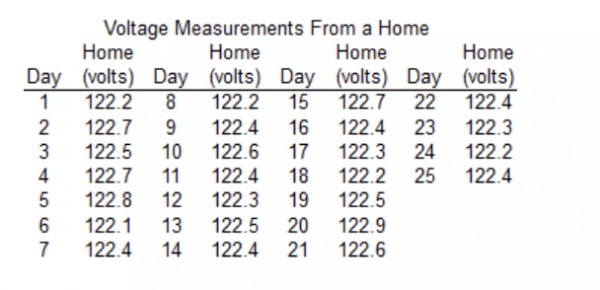
Does the result appear to have a normal? distribution? Why or why? not?
A supernova is almost always associated with
a. a very massive star. b. a very young star. c. a star undergoing helium flash. d. a white dwarf in a close binary system. e. a solar-like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium.
Excimer laser radiation from KrF 248 nanometer (nm) broad beam can produce ozone from air.(76) Discuss whether the lofting of low-level satellites containing excimer lasers could be used to restore the ozone layer
What will be an ideal response?