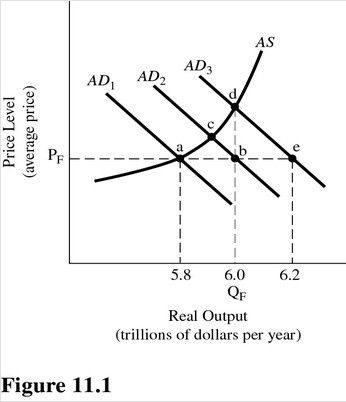
 Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is initially represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. If aggregate demand increases by the amount of the GDP gap, equilibrium will occur at
Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is initially represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. If aggregate demand increases by the amount of the GDP gap, equilibrium will occur at
A. Point a.
B. Point b.
C. Point c.
D. Point d.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Tony's Pizza's production function is shown in the table above. a) Suppose Tony operates Plant 2. He hires 2 workers and produces 20 pizzas a day. Is the pizzeria technologically efficient? Why or why not? b) Suppose Tony operates Plant 1
He hires 2 workers and produces 18 pizzas per day. Is Tony's Pizza technologically efficient? Why or why not? Can Tony increase production to 22 pizzas a day in the short run? If yes, how? c) Suppose Tony operates Plant 3. What is the marginal product of labor when the fourth worker is hired? When operating Plant 3, does Tony experience diminishing marginal returns? Explain. d) Suppose Tony currently uses Plant 3. Can he increase production from 40 to 50 pizzas per day in the short run? In the long run? If yes, how?
Suppose that the supply of insulin is perfectly elastic and the demand for insulin perfectly inelastic. Then the result of an excise tax would be
A. a significant increase in government revenue and a significant decrease in the quantity consumed. B. a significant decrease in the quantity consumed with no change in government revenue. C. a significant increase in government revenue and no change in the quantity consumed. D. no increase in government revenue and no change in the quantity consumed.
A nation's aggregate expenditure decreases with an increase in imports, other things constant
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The price elasticity of demand
a. is determined by the Federal Reserve Bank at a monthly meeting. b. only works well in competitive markets. c. intersects with the price elasticity of supply to determine the market equilibrium. d. is equal to the slope of the demand curve. e. varies from one point to another on a typical demand curve.