When the price level rises and the money wage rate does not change,
A) the quantity of potential GDP increases because the quantity of real GDP supplied increases.
B) the quantity of real GDP supplied increases as more businesses start up and potential GDP does not change.
C) existing businesses do not change their level of output.
D) profits fall and more businesses fail.
E) the quantity of real GDP supplied decreases as more businesses fail and potential GDP does not change.
B
You might also like to view...
The Great Depression is still the subject of controversy, including the question(s) of
(a) what caused the initial downturn. (b) why the economy contracted for so long (1929 to 1932) and why it contracted so much (real GNP fell about 30%). (c) whether government policy helped or hindered the recovery attempt. (d) all of the above.
Which of the following is most likely to be a feature of a state-contingent contract?
A) The agent pays the principal a higher licensing fee when demand is high compared to when demand is low. B) The agent makes the same wage regardless of demand. C) The agent, who lives in Nevada, earns more money on out-of-state sales (e.g., sales to California or New York) than in-state sales. D) The restaurant owner (principal) pays the waiter (agent) more when it is snowing or raining outside.
All of the following affect the demand elasticity for labor EXCEPT
A) final product income elasticity. B) ease of substitution of labor for other inputs. C) final product price elasticity. D) labor costs as a portion of total cost.
Refer to the diagram. Assume that nominal wages initially are set on the basis of the price level P 2 and that the economy initially is operating at its full-employment level of output Q f . In the long run, an increase in the price level from P 2 to P 3 will:
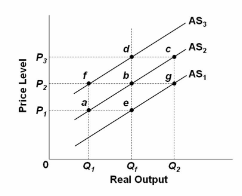
A. increase real output from Q f to Q 2 .
B. change aggregate supply from AS 2 to AS 1 .
C. decrease real output from Q 2 to Q 1 .
D. move the economy from b to d.