Suppose a market is initially in equilibrium and supply increases. The consumer surplus will:
a. be higher since the price is lower and equilibrium moves down along the demand curve.
b. be higher, since the price is lower and will move you down along the demand curve.
c. be higher since the price is lower and equilibrium moves up along the demand curve.
d. be lower since the price is lower and equilibrium moves up along the demand curve.
Answer: b. be higher, since the price is lower and will move you down along the demand curve.
You might also like to view...
Metering is
a. A type of indirect price discrimination b. A type of direct price discrimination c. An evaluation of a product d. An example of bundling
Exhibit 16-3 Money market demand and supply curves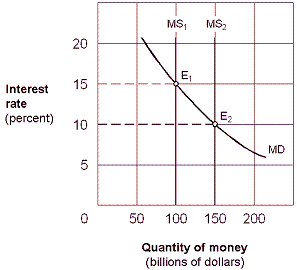
A. open market sale of securities by the Fed. B. higher discount rate set by the Fed. C. higher required-reserve ratio set by the Fed. D. open market purchase of securities by the Fed.
Expenditure-reducing policies designed to improve a current account deficit
A) turn domestic spending towards domestic goods. B) reduce the overall level of demand in the economy. C) turn domestic spending towards foreign goods. D) increase the overall level of demand in the economy.
Where Y is GDP, C is consumption, I is investment, G is government purchases, T is net taxes, and there is no international trade, private saving equals:
A. Y - T - C. B. Y -T - G. C. Y - C - I. D. C + I + G - T.