In 2007, 100 Japanese yen purchased $0.88 U.S. and in 2010, it purchased $0.93 U.S. Therefore, $1.00 U.S. was worth _____ yen in 2007 and _____ yen in 2010
a. 88; 93
b. 100; 114
c. 113.6; 107.5
d. 112.4; 105.3
c
You might also like to view...
Assuming all else equal, if the real interest rate increases, it will lead to:
A) a decrease in the quantity of credit demanded by a firm. B) a rightward shift of the credit demand curve of a firm. C) a leftward shift of the credit demand curve of a firm. D) an increase in the quantity of credit demanded by a firm.
If supply is upward-sloping and demand is downward sloping, what happens to the equilibrium real risk-free interest rate and quantity of real loanable funds per time period if there is a decrease of financial international capital flows into a nation:
a. The real risk-free interest rate rises and the quantity per time period falls. b. The real risk-free interest rate rises and the quantity per time period rises. c. The real risk-free interest rate falls and the quantity per time period falls. d. The real risk-free interest rate rises and the quantity per time period does not change. e. The real risk-free interest rate rises and the quantity per time period is uncertain.
If marginal benefits exceed marginal costs, it is profitable to:
A. decrease Q. B. increase Q. C. stay at that level of Q. D. All of the statements associated with this question are correct.
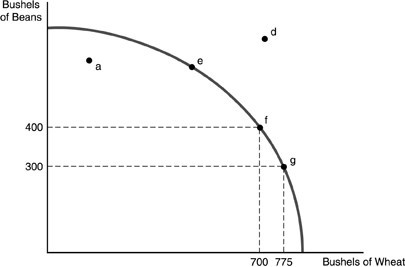 Refer to the above figure. The shape of the production possibility curve indicates that production of
Refer to the above figure. The shape of the production possibility curve indicates that production of
A. wheat is characterized by increasing costs while the production of beans is characterized by decreasing costs. B. both goods are characterized by decreasing costs. C. both goods are characterized by increasing costs. D. wheat is characterized by decreasing costs while the production of beans is characterized by increasing costs.