Assume that a perfectly competitive market is in long-run equilibrium. Suppose as a result of a health hazard associated with the industry's product, demand decreases drastically. What is the immediate result of this event?
A) The market price falls and the typical firm suffers an economic loss.
B) The market supply increases to offset the fall in demand.
C) The typical firm's average total cost curve shifts downward.
D) The typical firm's marginal cost curve shifts to the left.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large increase in government purchases will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; higher; potential B. recessionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; lower; lower D. expansionary; higher; higher
Describe the two basic strategies of unions in increasing wage rates for their members.
What will be an ideal response?
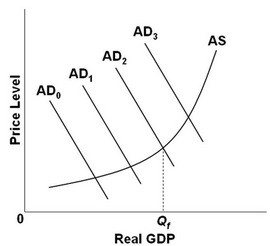 Refer to the above diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD0, it would be appropriate for the government to:
Refer to the above diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD0, it would be appropriate for the government to:
A. increase government expenditures or reduce taxes. B. reduce government expenditures or increase taxes. C. reduce government expenditures and taxes by equal-size amounts. D. reduce unemployment compensation benefits.
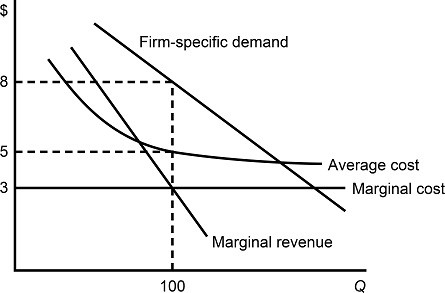
 Figure 8.4 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. If the firm's demand curve shifts to the left as more firms enter the market:
Figure 8.4 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. If the firm's demand curve shifts to the left as more firms enter the market:
A. the firm's profit will be smaller at the new profit-maximizing output level. B. the firm's profit will be greater at the new profit-maximizing output level. C. the firm's profit will remain the same at the new profit-maximizing output level. D. There is not sufficient information.