What are the main features of the Sherman Act?
What will be an ideal response?
The Sherman Act was passed in 1890, and it made it illegal to monopolize a market or engage in practices that result in a restraint of trade.
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 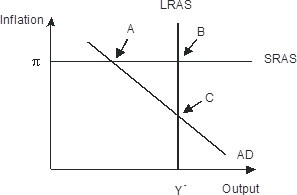
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
Why are property rights so important for markets?
A. Property rights allow companies to have a monopoly. B. Without property rights there are few incentives to improve, create, or build something, because you cannot legally trade it. C. Property rights force others to pay you more for the good or service. D. Those who have property rights are more likely to create more because they will get more money in the market.
The Fed increases the money supply by buying securities for $300 million. The impact of this increase, in the long-run, would be to
A. raise the average price level and increase the level of real GDP. B. raise the average price level, but real GDP (output) would stay the same. C. raise the real supply of loanable funds, lower the interest rate, and increase the demand for output. D. raise the real supply and demand for loanable funds with an increase in the interest rate.
If the equilibrium price of a good decreases, then consumer surplus will:
a. increase because existing consumers will now pay less for the good b. decrease because existing consumers will leave the market. c. decrease because the marginal utility derived from the good will fall. d. increase because the opportunity cost of consuming the good will increase.