The aggregate savings in an economy is $1,750 and the GDP of the economy is $55,000. The savings rate in the economy is:
A) 1.8%. B) 3.15%. C) 10%. D) 8.96%.
B
You might also like to view...
Hotelling's model has been used to describe differentiation in the political "market." Suppose that 100 voters are evenly distributed between the extreme left and the extreme right on the political spectrum, and that all voters vote, and they always vote for the candidate closest to them on this spectrum. The numbers on this spectrum represent the number of voters lying to the left of the number. So, at the midpoint, fifty voters lie to the left and fifty to the right. At the extreme right end, all 100 voters lie to the left. 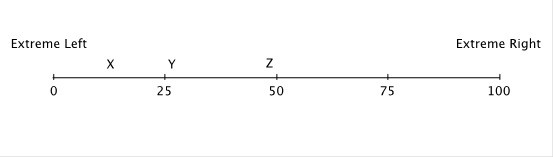 If Candidate X is running for office against Candidate Z, then:
If Candidate X is running for office against Candidate Z, then:
A. all voters to the left of Z will vote for X, and all voters to the right of Z will vote for Z. B. all voters who would have voted for Y will vote for X. C. Candidate X might win. D. Candidate Z will win.
Suppose that Country A has an absolute advantage over Country B in the production of both wheat and cloth. The opportunity cost of 1 unit of wheat is 2 units of cloth in Country A and 3 units of cloth in Country B. It follows that production of both wheat and cloth will be maximized if
a. Country A specializes in cloth. b. Country A specializes in wheat. c. Country A produces both goods. d. both countries produce both goods.
Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. b. Real GDP rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more positive (or less negative). c. Real GDP rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive). d. Real GDP falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive). e. Real GDP and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending remain the same.
When examining the financial status of households, wealth is
A) synonymous with income. B) a flow variable whereas income is a stock variable. C) a stock variable and includes both tangible assets and human capital. D) not as important as income because wealth does not change over time.