Suppose the quantity of money is greater than the quantity of money demanded. In the short run, what occurs to set the quantity of money equal to the quantity of money demanded?
What will be an ideal response?
In the money market, the interaction between the supply of money and the demand for money determines the equilibrium nominal interest rate. The quantity of money available is greater than the quantity of the money demanded when the nominal interest rate is above the equilibrium interest rate. When this occurs, in an effort to decrease the amount of money to the quantity people want to hold, people buy bonds with the excess. As a result, the demand for bonds increases. The price of bonds rises and the interest rate falls. When the nominal interest rate reaches its equilibrium, there is no longer an excess supply of money because at the equilibrium nominal interest rate, the quantity of money supplied equals the quantity demanded.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question.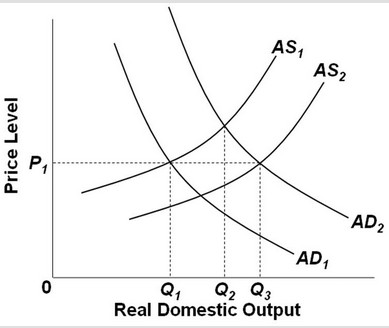 In the figure, AD1 and AS1 represent the original aggregate supply and demand curves. If Q1 is full-employment output, then AD2 and AS1 represent a(n) ________.
In the figure, AD1 and AS1 represent the original aggregate supply and demand curves. If Q1 is full-employment output, then AD2 and AS1 represent a(n) ________.
A. full-employment B. price stability C. expansion D. recession
Refer to the figure above. The triangular region ABC represents the ________
A) deadweight loss due to the presence of a pecuniary externality B) deadweight loss due to the presence of a negative externality C) economic loss of not recognizing a positive externality D) inefficiency created by not recognizing a negative externality
At the profit-maximizing level of production of a monopolist, ________
A) marginal revenue equals marginal cost B) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost C) marginal revenue is less than marginal cost D) both marginal revenue and marginal cost are negative
Economists use elasticity as a tool to measure
a. the relationship between people's attitudes and their income b. the relationship between people's willingness to supply a good and their willingness to demand that good c. people's sensitivity to changes in price or income d. the effect of changes in supply on people's willingness to demand goods e. the effect of changes in supply on the government's ability to tax