Microscopic slush in water tends to make the water
A) more dense.
B) less dense.
C) slipperier.
D) warmer.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A 5.0-kg object is suspended by a string from the ceiling of an elevator that is accelerating downward at a rate of 2.6 m/s2 . What is the tension in the string?
a. 49 N b. 36 N c. 62 N d. 13 N e. 52 N
Express the following number to three significant figures: 21.25 m
What will be an ideal response?
Over geological time periods, the Earth's climate has been
A) relatively stable B) continuously unstable C) constant and unchanging D) gradually becoming more unstable
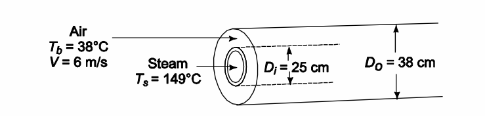
If the total resistance between the steam and the air (including the pipe wall and scale on the steam side) in Problem 7.36 is 0.05 m2 K/W, calculate the temperature difference between the outer surface of the inner pipe and the air. Show the thermal circuit.
GIVEN
Atmospheric flow through an annulus with steam condensing in inner tube
Diameters Inside
(Di) = 25 cm = 0.25 m
Outside (Do) = 38 cm = 0.38 m
Steam temperature (Ts) = 149°C
Air velocity (V) = 6 m/s
Total resistance between the steam and air (At Rtot) = 0.05 (m2 K)/W
Air bulk temperature (Tb) = 38°C
From Problem 7.36 heat transfer coefficient on the outer surface of the inner pipe (c h) = 25.4 W/(m2 K)
FIND
The temperature difference between the outer surface of the inner pipe and the air (?T)
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Steam temperature is constant and uniform
Heat transfer to the outer surface is negligible
Air temperature given is the average air temperature
Thermal resistance of inner tube wall and condensing steam is negligible (Inner tube wall surface
temperature = Ts)
SKETCH