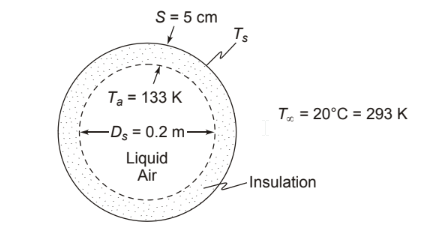
A sphere 20 cm in diameter containing liquid air (–140°C) is covered with 5-cm-thick glass wool (50 kg/m3 density) with an emissivity of 0.8. Estimate the rate of heat transfer to the liquid air from the surrounding air at 20°C by convection and radiation. How would you reduce the heat transfer?
GIVEN
• A sphere containing liquid air covered with glass wool
• Sphere diameter (Ds) = 20 cm = 0.2 m
• Liquid air temperature (Ta) = – 140°C = 133 K
• Surrounding air temperature (T?) = 20°C = 293 K
• Insulation thickness (s) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
• Insulation emissivity (?) = 0.8
FIND
• Rate of heat transfer from liquid air to surrounding air
(q)
• How can this be reduced?
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state conditions
• The surroundings behave as a black body enclosure at T?
• Surrounding air is still
• Thermal resistance of the convection inside the sphere and of the container wall are negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4).
the thermal conductivity of glass wool (ki) = 0.037 W/(m K)
The natural convection heat transfer coefficient on the exterior of the insulation depends on the exterior temperature of the insulation (Ts), an iterative procedure is therefore required. For the first iteration, let Ts = – 20°C (253 K)
for dry air at the mean temperature of 0°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00366 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0237 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 13.9 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The characteristic length for the sphere is
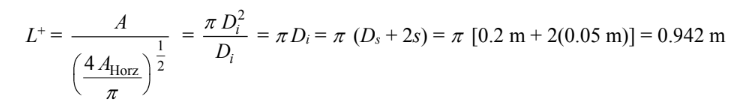
The Grahsof and Rayleigh numbers based on this length are
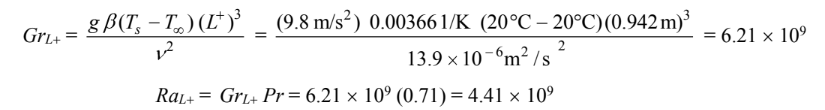
Although the empirical relation extends only to Ra+ = 1.5 × 109, it will be extrapolated here to estimate the Nusselt number

The thermal circuit for the sphere is shown below
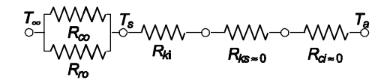
where Rci = interior convective resistance (negligible)
Rks = conductive resistance of the container (negligible)
Rki = conductive resistance of the insulation
Rco = exterior convective resistance
Rro = exterior radiative resistance

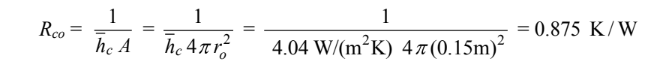
The exterior radiative resistance is
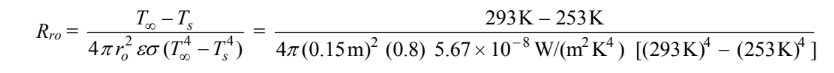
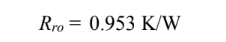
The net resistance for the thermal network is Rt = Rki + Ro where
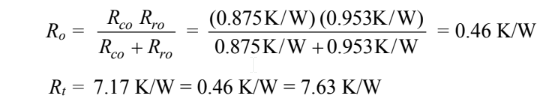
The rate of heat transfer is given by
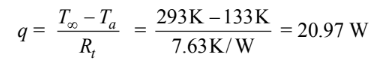
The accuracy of the insulation surface temperature guess can be checked from
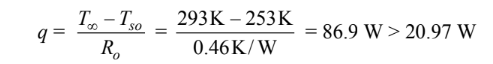
Therefore, we need to reduce Tso. However, notice that nearly 94% of the total thermal resistance is due to the insulation. This means that adjusting Tso has little effect on the total rate of heat transfer. It also means that the heat gain by the liquid air can be most easily reduced by increasing the thickness of insulation, selecting an insulation with lower thermal conductivity, or both.
You might also like to view...
Gravitational Potential Energy: An 825-kg space vehicle is circling Earth in a circular orbit with a radius of 10,300 km. Its orbit is to be changed to a larger circle with a radius of 17,400 km. How much energy is required to accomplish this? The mass of Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2.
A. 1.00 × 109 J B. 1.30 × 1010 J C. 6.51 × 109 J D. 4.45 × 109 J E. 4.50 × 1010 J
What do astronomer's mean when they say that Earth is not in a special spot?
A. All space is expanding so Hubble's law would apply around all galaxies. B. The Big Bang explosion sent all material blasting away from the Earth. C. Hubble measured the expansion law from the Moon, not from the Earth. D. Hubble's law applies to some galaxies but not to others, so many planets besides Earth have their own Hubble's law. E. The Sun is at the center of the universe, but the Earth is not.
The single most important determinant of the temperature, density, radius, luminosity, and pace of evolution of a protostar is its:
A) chemical composition. B) magnetic field. C) spin. D) mass. E) molecular composition.
Why doesn't a car driven at 200 km/h emit twice as much pollution in a 400 km trip as a car traveling at 100 km/h?
What will be an ideal response?