Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 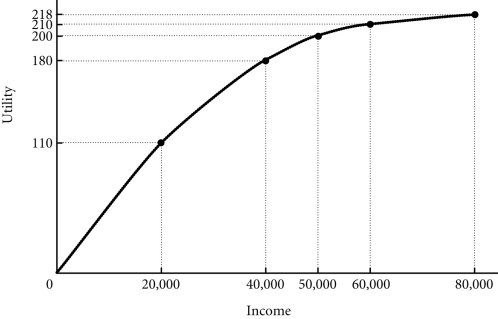 Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. John has two job offers when he graduates from college. John views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $50,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. John believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. What is the expected value of John's income for each job offer?
Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. John has two job offers when he graduates from college. John views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $50,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. John believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. What is the expected value of John's income for each job offer?
A. $50,000 for the first offer and $50,000 for the second offer
B. $50,000 for the first offer and $80,000 for the second offer
C. $50,000 for the first offer and $30,000 for the second offer
D. $25,000 for the first offer and $50,000 for the second offer
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
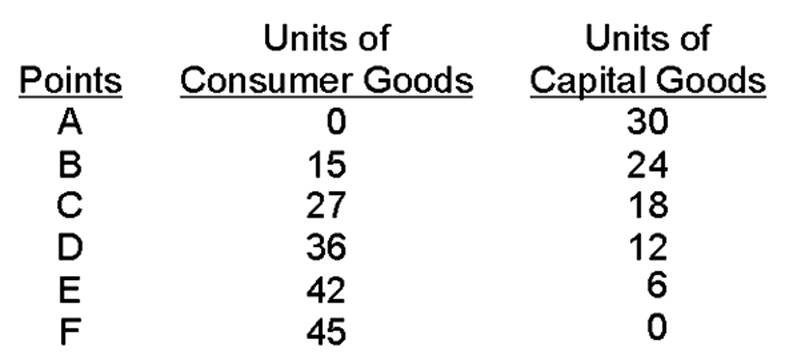
If the economy is producing at point B, the opportunity cost of gaining 12 units of consumer goods is _______ units of capital goods.
If a buyer's reservation value for a good is $15 and the price at which he purchases the good is $8, his consumer surplus is:
A) $7. B) $1.8. C) -$7. D) $120.
Since 1972, the world price of oil has been largely determined by OPEC, which controls about 75 percent of the world's proven oil reserves. Since 1972 the price of oil has
A) fluctuated. OPEC's situation is an example of a prisoner's dilemma. B) risen slowly, but steadily. Members of OPEC fear that if they raise the price of oil too quickly this will lead oil-buying nations to accuse OPEC of price gouging, which is illegal under international law. C) been tied by OPEC to the rate of inflation in the United States. If, for example, the rate of inflation is 5 percent in one year, OPEC will raise the price of oil by 5 percent the next year. D) steadily fallen through the 1970s, then risen continually in the years since then. OPEC's actions are an example of implicit collusion.
The transaction motive for holding money
A. varies inversely with income. B. varies directly with the number of times one is paid annually. C. are used to make expected expenditures. D. are held for the same reasons that precautionary cash balances are held.