Frank is purchasing products C and D in utility-maximizing amounts. If the price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2, then:
A. the marginal utility of D is twice that of C.
B. the marginal utility of D is the same as that of C.
C. the marginal utility of C is twice that of D.
D. the marginal utility of C is four times that of D.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is downward sloping
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following helps explain how the multiplier and crowding-out effect impact the size of the shift in aggregate demand from a tax change
a. Tax cuts stimulate consumer spending, earnings and profits rise, which further stimulates consumer spending—the multiplier effect. b. The higher income leads to an increase in the demand for money, which tends to lead to higher interest rates. c. The higher interest rates make borrowing more costly and reduce investment spending—the crowding-out effect. d. All of the above
The general approaches to global poverty reduction include all of the following except
A. Redistribution of incomes within countries. B. Redistribution of incomes across nations. C. An increase in government control of resources. D. Economic growth that raises average incomes.
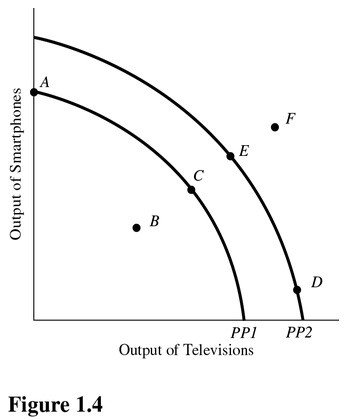 In Figure 1.4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
In Figure 1.4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A. Implementation of training programs that improve the skills of workers. B. A flu epidemic that makes many workers sick. C. Tougher pollution controls for the producers of televisions and smartphones. D. An increase in the unemployment rate.