Suppose one is offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 half the time but lose $1,000 half the time. Since in this case one is as likely to win as to lose the $1,000, the average payoff on this gamble—its expected value—is:
0.5 ? $1,000 + 0.5 ? (-$1,000 ) = 0.
Under such circumstances:
A) no one will take the gamble.
B) risk averse individuals will take the gamble.
C) risk lovers individuals will not take the gamble.
D) risk neutral individuals will not take the gamble.
E) risk lovers and risk neutral individuals may take the gamble.
E
You might also like to view...
The net international investment position reflects the domestic holding of foreign assets minus foreign holdings of domestic assets
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
If real equilibrium GDP is above potential GDP, expansionary fiscal policy should be pursued
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following changes to the market in the graph shown could cause the price ceiling to become non-binding?
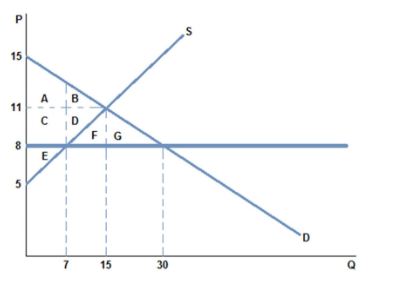
A. Demand could increase, and shift to the right.
B. Supply could increase, and shift to the left.
C. Supply could increase, and shift to the right.
D. Supply could decrease, and shift to the left.
If individuals make intertemporal choices using "hyperbolic discounting", this may create inefficient choices because individuals will: a. not take account of their time preferences
b. make choices that are inconsistent over time. c. have a preference for only consuming in the future. d. confuse nominal and real interest rates.