The heat loss from the hairdryer duct enclosure was neglected. To a designer, while this may appear to be reasonable assumption it should really be checked bu order of magnitude calculations even if all the parameters are not known. In order to determine whether the heat loss from the exterior of the duct enclosure is neglected or not, assume a high surface emissivity of 0.8, an average surface temperature of 400C, and consider an estimate for natural convection coefficient at a high reasonable value. If the length of hair dryer is 20 cm, calculate the expected heat loss per unit length of the dryer duct, compare it with heat dissipation per unit length from the internal electrical heating, and comment on validity of negligible heat loss assumption.
GIVEN
- High surface emissivity of 0.8, an average surface temperature of 400C
- Length of the hear drier L=20 cm =0.2 m
FIND
- Expected heat loss per unit length of dryer duct
- Compare it with heat dissipation per unit length from the internal electrical heating.
ASSUMPTIONS
- Steady state conditions prevail
- Heat loss from outside of dryer duct is neglected.
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the air properties are
Convection heat transfer coefficient for air (considering higher value) (hc)=20 W/(m2 K)
Specific heat capacity(Cp)= 1.0049 kJ/kgK
Heat radiation from body grey body of average temperature of 400C=313 K to ambiance of 220C
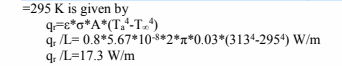
Heat transferred by natural convection is given by
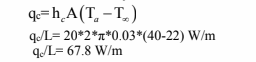
Heat dissipation per unit length of dryer from internal electrical heating is given by
Q/L=110.5/0.2= 552.2 W/m
You might also like to view...
The electric field along the axis of a ring-shaped charge of total charge Q distributed uniformly is given by E = Qx/(4? ?0 (x2+ a2)3/2 )
where a is the radius of the ring and x is the distance from the center of the ring. The electric field at the center of the ring is zero and at great distances from the ring approaches zero. At what position is the electric field a maximum for positive values of x?
What behavior of muons moving through Earth's atmosphere was different compared to muons at rest in a way that helped confirm time dilation?
a. They moved a shorter distance in Earth's reference system than in their own. b. Their size was smaller as seen from Earth's reference system. c. Their arrival in Earth's atmosphere and their detection on the ground were no longer synchronized. d. Their speed was different as seen in Earth's reference system and in the reference system in which they were at rest. e. They lived longer as shown by traveling farther before decay in Earth's reference system.
Series/Parallel Circuits: In the circuit shown in the figure, the resistor R has a variable resistance. As R is decreased, what happens to the currents?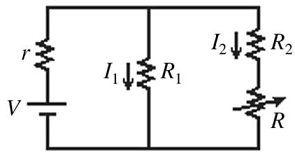
A. I1 remains unchanged and I2 increases. B. I1 decreases and I2 decreases. C. I1 decreases and I2 increases. D. I1 increases and I2 decreases. E. I1 increases and I2 increases.
A small steel sphere falls with a terminal velocity in a viscous fluid of 2.00 cm/s. If the radius of the steel sphere is doubled, then what is the terminal velocity of the sphere?
A. 1.00 cm/s B. 2.00 cm/s C. 4.00 cm/s D. 6.0 cm/s E. 8.00 cm/s