In the circular flow, an increase in the money supply tends to result when
a. planned I equals planned S.
b. planned I is less than planned S.
c. planned I is greater than planned S.
d. there is a surplus government budget.
c. planned I is greater than planned S.
You might also like to view...
What is the principal-agent problem?
A) It is a problem caused by a person (principal) who hires an agent to act on his behalf but is unwilling to delegate authority to the agent to carry out the task in the best possible way. B) It is a problem of the power system of boss and subordinate where the boss (principal) exerts influence over his subordinates (agents) using punishment or threat. C) It is a problem that exists when a person (principal) has more information about the task than the agent he hires to perform the task. D) It is a problem caused by agents pursuing their own interests rather than the interests of the principals who hired them.
Everything else held constant, in the market for reserves, when the federal funds rate is 1%, increasing the interest rate paid on excess reserves from 1% to 2%
A) lowers the federal funds rate. B) raises the federal funds rate. C) has no effect on the federal funds rate. D) has an indeterminate effect on the federal funds rate.
Government-run employment agencies and public training programs are operated by the government to try to facilitate job search and reduce unemployment
a. Almost all economists agree that such programs are of no use. b. Almost all economists agree that such programs work very well. c. Some economists claim that the government can do these things no better than firms and individuals could do them for themselves. d. Some economists claim that these programs increase frictional unemployment.
Figure 11-2
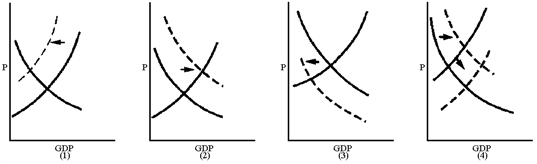
Which graph in Figure 11-2 best reflects a Keynesian's view of the short-run impact of an increase in the personal income tax rate?
a.
1
b.
2
c.
3
d.
4