The cross elasticity of demand between apples and oranges is defined as the
A) percentage change in the quantity of apples demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of oranges.
B) price elasticity of demand for apples divided by the price elasticity of demand for oranges.
C) percentage change in the quantity of apples demanded divided by the percentage change in the quantity of oranges demanded.
D) change in the quantity of apples demanded divided by the change in the quantity of oranges demanded.
A
You might also like to view...
The following graph depicts demand.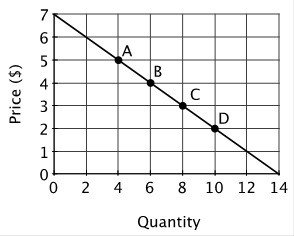 The slope of the demand curve (ignoring the negative sign) is:
The slope of the demand curve (ignoring the negative sign) is:
A. 1. B. 2. C. 0.5. D. 1.5.
The self-correcting tendency of the economy means that rising inflation eventually eliminates:
A. unemployment. B. exogenous spending. C. recessionary gaps. D. expansionary gaps.
Since most banks have positive gaps and negative duration gaps, an increase in market interest rates will
A) increase bank profits and increase bank capital. B) increase bank profits and decrease bank capital. C) decrease bank profits and increase bank capital. D) decrease bank profits and decrease bank capital.
When the Fed sells bonds in the open market, in the product market (the aggregate demand- aggregate supply model),
A) real GDP will fall and the price level will rise. B) real GDP and the price level will rise. C) real GDP and the price level will fall. D) real GDP will rise and the price level will fall.