Compare and contrast the push and pull supply chain methods.
What will be an ideal response?
Pull supply chain is a supply chain in which requests for merchandise are generated at the store level on the basis of sales data captured by POS terminals. Basically, in this type of supply chain, the demand for an item pulls it through the supply chain. An alternative is a push supply chain, in which merchandise is allocated to stores on the basis of forecasted demand. Once a forecast is developed, specified quantities of merchandise are shipped (pushed) to DCs and stores at predetermined time intervals. In a pull supply chain, there is less likelihood of being overstocked or out of stock because the store requests for merchandise are based on customer demand.
You might also like to view...
When a sales journal is used, there is no need to keep a controlling account for Accounts Receivable in the general ledger
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
How many guitars does Ajax need to sell each month to break even? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole guitar.)
Ajax was a professional classical guitarist until a motorcycle accident left him disabled. After long
months of therapy, he hired an experienced luthier and started a small shop to make and sell Spanish
guitars. The guitars sell for $800, and the fixed monthly operating costs are as follows:
![]()
Ajax's accountant told him about contribution margin ratios, and Ajax understood clearly that for every
dollar of sales, $0.60 went to cover his fixed costs, and anything above that point was profit.
A) 5 guitars
B) 3 guitars
C) 7 guitars
D) 8 guitars
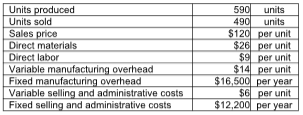
There are no beginning inventories. What is the ending balance in Finished Goods Inventory using variable costing?
McFarlane, Inc. reports the following information:
A) $4900
B) $3500
C) $5500
D) $7697
Which one of the following is not an organizational factor that contributes to power corruption?
a. Formal and closed communication. b. Focus on short-term goals. c. Performance-based hiring. d. Centralized decision making.