Which of these highlights the advantages of more widespread participation in the electoral process?
A) The needs of once-excluded groups are now given at least some consideration.
B) Citizens are much happier with government and government policies.
C) More elections and greater participation make it easier to plan for the long run.
D) Greater participation leads to easier compromises between disparate groups.
E) Citizens increase their participation when more opportunities are provided.
A
You might also like to view...
In______________, the Supreme Court upheld by a 5-to-4 margin the power of a state to regulate the retail price of milk
a. Home Building and Loan Association v. Blaisdell (1934) b. Nebbia v. New York (1934) c. United States v. Butler (1936) d. West Coast Hotel Company v. Parrish (1937)
Local governments, including single-purpose districts, gain their power to function and establish their operating structure through
a. home rule. b. citizen initiative petition. c. eminent domain. d. an act of Congress.
Which of the following is not organized as a federal state?
A) United States B) Canada C) France D) Germany E) Mexico
What is the ideological position of the median voter in Figure 1?
Figure 1 illustrates an election in which there are seven voters (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) arrayed along a single left–right issue dimension that runs from 0 (most left) to 10 (most right). Each voter is assumed to have a single-peaked preference ordering over the issue dimension and to vote for the party that is located closest to her ideal point. The voters are participating in a majority rule election in which there are two parties, P1 and P2, competing for office.These parties can be thought of as “office-seeking” parties since they only care about winning the election and getting into office.
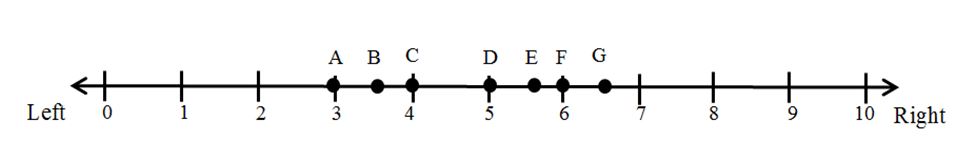
A. 1.5
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 5.5
G. 7
H. 8