Suppose an American worker can make 50 pairs of gloves or grow 300 radishes per day. On the other hand, a Bangladeshi worker can produce 100 pairs of gloves or grow 200 radishes per day. The opportunity cost of one pair of gloves is:
A. 6 radishes for the United States and 2 radishes for Bangladesh.
B. 60 radishes for the United States and 20 radishes for Bangladesh.
C. 1/6 radishes for the United States and ½ radishes for Bangladesh.
D. 6,000 radishes for the United States and 2,000 radishes for Bangladesh.
A. 6 radishes for the United States and 2 radishes for Bangladesh.
You might also like to view...
________ is defined as a market outcome in which the marginal benefit to consumers of the last unit produced is equal to the marginal cost of production, and in which the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is at a maximum
A) Economic efficiency B) Consumer efficiency C) Deadweight efficiency D) Producer efficiency
In a simple closed economy, the income approach to calculating GDP is:
A. wages + interest + rental income + profits. B. wages + interest + government income + profits C. wages + government earned interest + rental income + profits D. wages + interest + rental income profits.
The factor of production that is always fixed in the short run is
a. the amount of raw materials b. the size of the physical plant c. the number of workers d. energy costs e. quantity of output
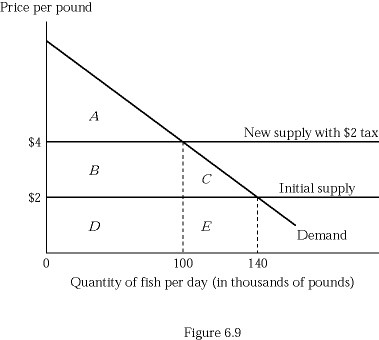 Figure 6.9 depicts a hypothetical fish market with a horizontal supply curve. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $2 per pound of fish, and the tax is paid in legal terms by producers. Which of the following statements is correct?
Figure 6.9 depicts a hypothetical fish market with a horizontal supply curve. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $2 per pound of fish, and the tax is paid in legal terms by producers. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Producers bear the full cost of the tax. B. Consumers bear the full cost of the tax. C. Both producers and consumers equally share the tax. D. Consumers bear a relatively large share of the tax, compared to producers.