In a coordination game, a Nash equilibrium occurs when
a. each player ignores the strategy of the other player
b. each player chooses no strategy, but maintains the status quo
c. each player chooses the same strategy
d. one player can improve the outcome by changing strategy
e. None of the answers is correct.
C
You might also like to view...
Railway engines create sparks, which sometimes set fire to crops planted near the tracks. A large number of farmers are affected, and transactions costs prevent the farmers and the railroad from negotiating bribes or side payments. The price of railway service is $250 per train, and each train causes $50 of crop damage. The accompanying diagram shows the relevant market for railway service.
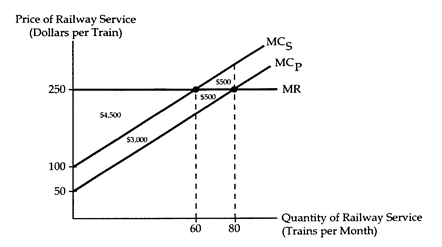
(i) Suppose a Pigovian tax of $50 per train is imposed on the railroad. By how much will social gain increase?
(ii) Suppose that the farmers can move their crops away from the tracks at a cost of $2,400 per month. If the goal is to achieve economic efficiency, who should be made liable for the crop damage? What will be the resulting social gain?
(iii) Suppose that farmers still have the option of moving their crops as described in part ii. Also suppose that the railroad can install safety equipment that will prevent the engine sparks at a cost of $25 per train. If the goal is to achieve economic efficiency, who should be made liable for the crop damage? What will be the resulting social gain?
Charlie is willing to pay $10 for a T-shirt that is priced at $9. If Charlie buys the T-shirt, then his consumer surplus is
A. $0.90. B. $19. C. $90. D. $1.
What is the macroeconomic consequence if firms accumulate large amounts of unplanned inventory at the beginning of a recession?
What will be an ideal response?
The Taylor rule specifies
a. a constant relationship between interest rates and output. b. a constant relationship between interest rates, output, and inflation. c. a flexible relationship between interest rates, output, and inflation. d. a fixed relationship between inflation and output. e. none of the above.