In the above figure, assume the economy starts out in equilibrium at point d. If the Fed increases the money supply so that the new aggregate demand curve is AD3, then the new short-run equilibrium will be at point
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) i.
C
You might also like to view...
Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour
Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 5 hours and her marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $36. If she is following the marginal principle, Krystal should A) stay open 1 more hour. B) stay open 2 more hours. C) stay open 1 fewer hour. D) stay open 2 fewer hours.
An increase in the demand for a good will tend to bid up the cost of acquiring the good more
A) if suppliers respond by quickly making larger quantities available. B) if the cost of transferring resources out of other uses into production are low. C) in the short run than in the long run. D) if the supply curve is highly elastic.
Refer to the graphs below. They show the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for a product. For which graph would a firm experience first economies and then diseconomies of scale over its range of output?
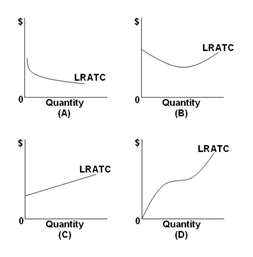
A. Graph A
B. Graph B
C. Graph C
D. Graph D
In general, the steeper the consumption schedule the:
A. Smaller is the marginal propensity to consume B. Greater is the marginal propensity to save C. Smaller is the multiplier D. Larger is the multiplier