When government provides a good with an external benefit, to attain efficiency the price paid by consumers is set equal to the
A) marginal private benefit at the efficient level of output.
B) marginal private cost at the efficient level of output.
C) amount paid by taxpayers.
D) market-determined price.
E) marginal external benefit at the efficient level of output.
A
You might also like to view...
We could increase the production of both heart transplants and round-the-world trips if we moved to point T from point
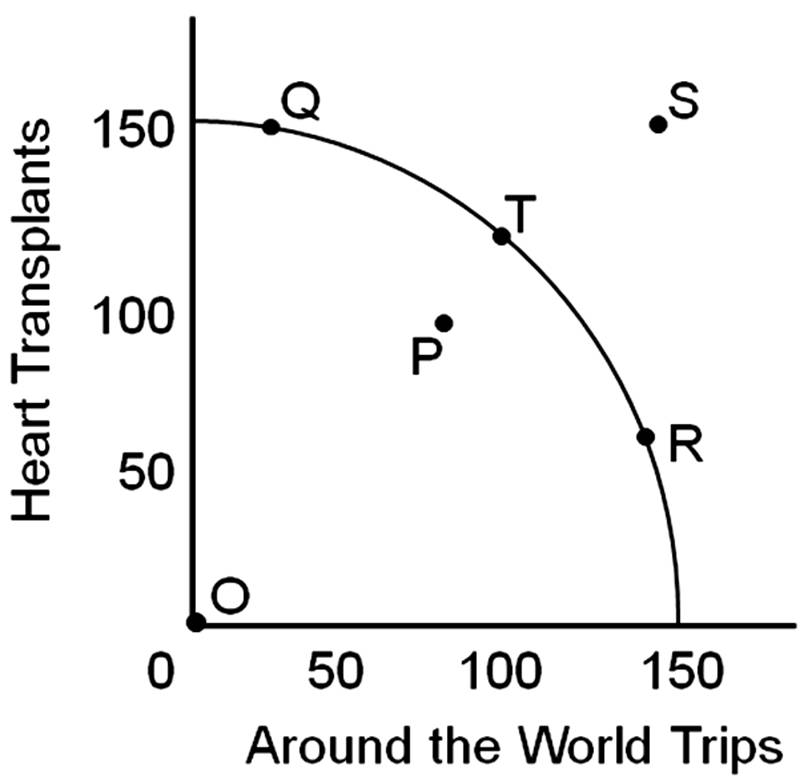
A. P.
B. Q.
C. R.
D. S.
What insights into the macroeconomic consequences of financial frictions arise from the new Keynesian model?
What will be an ideal response?
In the 1920s and 1930s, economists became increasingly aware that there were industries that did not fit the model of perfect competition or pure monopoly. Two separate theories of monopolistic competition resulted
Edward Chamberlin of Harvard published the Theory of Monopolistic Competition in 1933. Chamberlin defined monopolistic competition as A) a relatively large number of producers offering similar but differentiated products. B) a relatively small number of producers offering similar but differentiated products. C) a market situation in which a large number of firms produce identical products. D) a market situation in which a small number of firms produce similar products.
Exhibit 20-3 Money market demand and supply curves
?
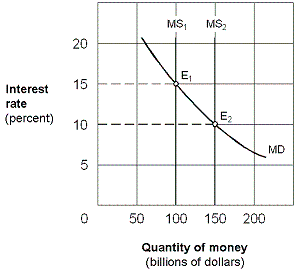
A. open market sale of securities by the Fed. B. higher discount rate set by the Fed. C. higher required-reserve ratio set by the Fed. D. open market purchase of securities by the Fed.