What is economic profit?
What will be an ideal response?
A firm's economic profit is its total revenue minus its total opportunity cost, which is the sum of explicit costs and implicit costs.
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. If a consumer demands the same (positive) amount of a good no matter what their income, then the income elasticity is also positive. 2. Normal goods have income elasticities greater than 1, while inferior goods have income elasticities less 3. Estimates of the price elasticity of demand depend, in part, on the units used to measure price and 4. The cross elasticity of demand will be positive when goods are substitutes and negative when goods are complements.
When there is no Equilibrium (or no Nash Equilibrium), we expect that:
a. the firms end up in the cooperative strategy. b. a firm will follow a randomized strategy. c. a firm will not care what it does. d. a firm will very likely have a dominant strategy.
How does the leftward shift of the supply curve in graph 2 affect the individual firm shown in graph 1?
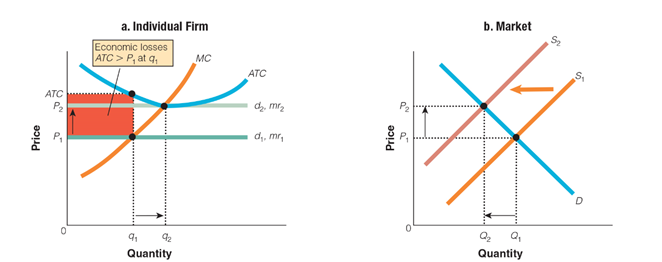
a. It causes the firm’s quantity of sales to decrease.
b. It causes the firm’s product price to increase.
c. It causes the firm to dip below its average total cost.
d. It causes the demand for the firm’s products to decrease.
Under average-cost pricing, an increase in the monopolist's production cost will:
A. decrease its profit because its profit per unit decreases. B. not affect its profit because the government adjusts the regulated price equal to the average cost. C. increase its profit because the monopolist can reduce the average cost at a greater output level. D. None of these