The nominal exchange rate is the:
A. market on which currencies of various nations are traded for one another.
B. quantity of foreign currency assets held by a government for the purpose of purchasing the domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
C. rate at which two currencies can be traded for each other.
D. price of the average domestic good or service relative to the price of the average foreign good or service, when prices are expressed in terms of a common currency.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Start-up costs:
A. have no impact on the number of firms in an industry because they are sunk costs. B. are the one-time costs incurred when beginning the production of a new product. C. are inversely related to variable costs. D. are always greater than marginal costs.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.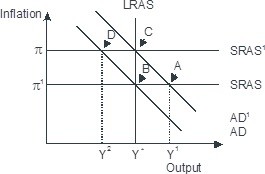
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
Special-interest legislation is legislation where there are both widespread costs and benefits
a. True b. False
Between 1960 and 1997, the federal budget was never in surplus
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false