A competitive market is in equilibrium. Then there is an increase in demand and an increase in supply. The equilibrium price ________, and the equilibrium quantity ________
A) rises; increases
B) perhaps changes but we can't say if it rises, falls, or stays the same; does not change
C) falls; increases
D) perhaps changes but we can't say if it rises, falls, or stays the same; increases
E) falls; perhaps changes but we can't say if it increases, decreases, or stays the same
D
You might also like to view...
What are the three forces that cause the aggregate demand curve to slope down? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
A learning curve relates ________ to ________ and is a case of ________ returns
A) unit cost; cumulative production; dynamic increasing returns B) output per time period; long-run marginal cost; dynamic increasing returns C) unit cost; cumulative production; dynamic decreasing returns D) output per time period; long-run marginal cost; dynamic decreasing returns E) labor productivity; education; increasing marginal returns
In 2011, the 20 percent of families with the lowest incomes paid an average federal tax rate (on all federal taxes) of about ________, whereas the 20 percent of families with the highest incomes paid an average tax rate of about ________.
A. 8.4 percent; 29 percent B. 10.3 percent; 30.9 percent C. 4.0 percent; 35 percent D. 1.9 percent; 23.4 percent
Refer to the below table for a certain product's market in Econland. If the world price of the product were $6 and a tariff of $1 per unit were applied to imports of the product, then the tariff would generate government revenues of:
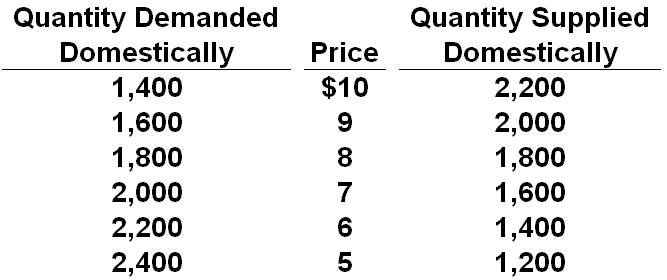
A. $600
B. $400
C. $800
D. $1,200