Successive bright fringes in an interference pattern result from
A) equal-length distances from the slits.
B) distance from the slits successively increasing one wavelength at a time.
C) destructive interference.
D) none of the above
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Two experiments are performed. In (A), an 18.0 N force pushes horizontally on a 2.00 kg block that then pushes on a 4.00 kg block. In (B), an 18.0 N force pushes on a 4.00 kg block that then pushes on a 2.00 kg block. Which statement is correct?
a. The acceleration is 3.00 m/s2 in both (A) and (B). b. The acceleration is 4.50 m/s2 in both (A) and (B). c. The acceleration is 6.00 m/s2 in both (A) and (B). d. The acceleration is 9.00 m/s2 in both (A) and (B). e. The 2.00 kg block has a 9.00 m/s2 acceleration. The 4.00 kg block has a 4.50 m/s2 acceleration.
In the color wheel shown below, which colors are the secondary colors?
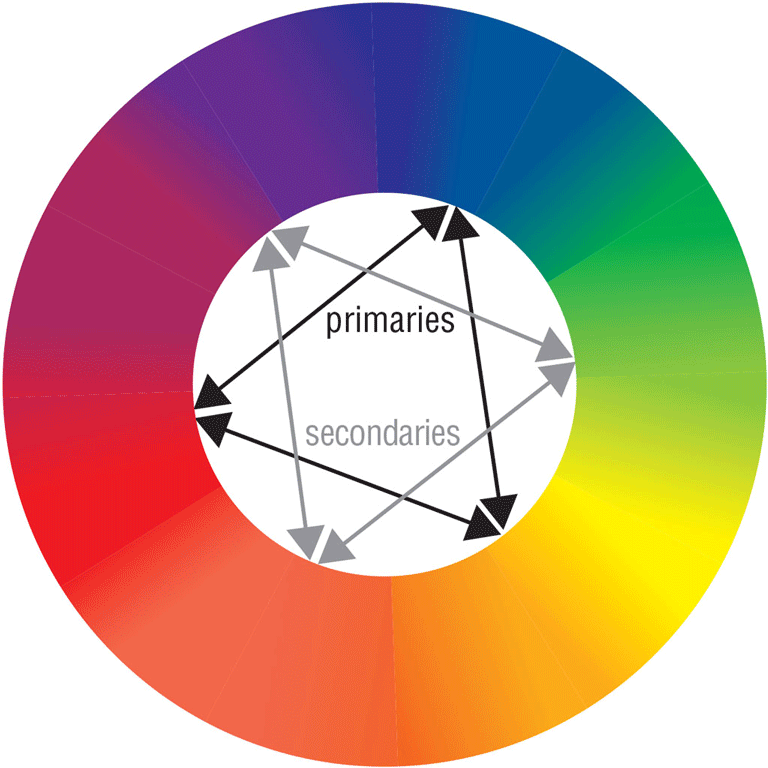
A. red, yellow, blue B. orange, green, purple C. green, blue, purple D. yellow, orange, red
The most detailed look we've had of an asteroid comes from:
A) spacecraft sent to an asteroid. B) ground based optical images. C) Earth orbital X-ray images. D) ground based radar images. E) high-altitude UV spectroscopy.
The luminosity class of a star tells an astronomer:
A) whether the star is close to us or far away B) whether or not the star is surrounded by planets C) whether the star is a supergiant, a giant, or a main-sequence star D) how long ago the star formed E) none of the above