The luminosity class of a star tells an astronomer:
A) whether the star is close to us or far away
B) whether or not the star is surrounded by planets
C) whether the star is a supergiant, a giant, or a main-sequence star
D) how long ago the star formed
E) none of the above
Answer: C) whether the star is a supergiant, a giant, or a main-sequence star
You might also like to view...
Lenz's Law: The wire in the figure carries a current I that is decreasing with time at a constant rate. The wire and the three loops are all in the same plane. What is true about the currents induced in each of the three loops shown?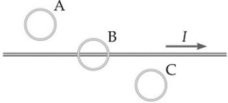
A. No current is induced in any loop. B. The currents are counterclockwise in all three loops. C. The currents are clockwise in all three loops. D. Loop A has clockwise current, loop B has no induced current, and loop C has counterclockwise current. E. Loop A has counterclockwise current, loop B has no induced current, and loop C has clockwise current.
By what factor should the length of a simple pendulum be changed if the period of vibration were to be quadrupled?
a. 16 c. 0.25 b. 4.0 d. 1/16
A bird sitting on a bare high-voltage wire is not electrocuted because
1) of the high resistance of its body. 2) of no electrical potential difference across its body. 3) its body is at a low electric potential compared to the wire. 4) the high voltage across its feet produces a very small current. If the bird stood on the wire with only one foot, it would 5) be electrocuted. 6) remain unharmed.
If an electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 9.9 kV, what is its resulting speed? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, k = 1/4??0 = 8.99 × 109 N • m2/C2, mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg)
A) 5.9 × 107 m/s B) 4.9 × 107 m/s C) 3.9 × 107 m/s D) 2.9 × 107 m/s