The principal of neutrality states that, with respect to economic decisions, all taxes must be neutral.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
False
You might also like to view...
An example of normative analysis is studying
a. how market forces produce equilibrium. b. surpluses and shortages. c. whether equilibrium outcomes are socially desirable. d. income distributions.
If health care spending is already on the flat of the curve, it may not be possible to improve health status by increasing spending. In this situation, the best way to improve health status may be to:
a. improve overall educational attainment so people can better follow the advice from the medical community. b. increase the availability of government health insurance. c. improve life-style decisions by reducing smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use. d. invest in biotechnology to determine the genetic factors that improve health. e. improve access to medical care.
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is $3, a perfectly competitive firm: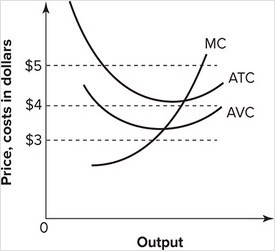
A. incurs a loss but can still cover its variable costs and some of its fixed costs. B. earns a profit. C. breaks even. D. incurs a loss and cannot cover its variable costs.
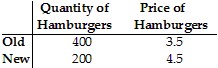 Table 5.1Refer to Table 5.1. A change in the price of hamburgers caused the change in quantity demanded shown in the table. The price elasticity of demand for hamburgers (calculated using the initial value formula) is:
Table 5.1Refer to Table 5.1. A change in the price of hamburgers caused the change in quantity demanded shown in the table. The price elasticity of demand for hamburgers (calculated using the initial value formula) is:
A. 0.25. B. 0.50. C. 1. D. 1.75.