Making optimal decisions "at the margin" requires
A) making consistently irrational decisions.
B) weighing the costs and benefits of a decision before deciding if it should be pursued.
C) making decisions according to one's whims and fancies.
D) making borderline decisions.
B
You might also like to view...
While the price of a resource may increase sharply during some periods, the structure of ____ accompanying the price increase makes depletion highly unlikely and provides the seeds for future reversal
a. government programs b. foreign competition c. incentives d. taxation
If the price of rubber (an input to the production of tires) increases:
A. the supply of tires will increase. B. the demand for tires will decrease. C. the supply of tires will decrease. D. the demand for tires will increase.
In this graph for the marginal costs and benefits of pollution controls, at output level Q*, pollution control is ______.
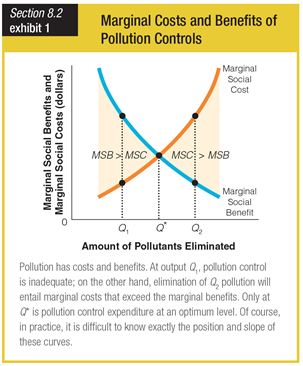
a. unnecessary
b. optimized
c. insufficient
d. excessive
In the circular flow model, households
A) sell goods and services in the input market. B) and firms spend earnings from resource sales on goods and services in the factor market. C) hire resources sold by firms in the factor market. D) spend earnings from resource sales on goods and services in the product market.