In which market model is there mutual interdependence?
A. monopolistic competition
B. pure monopoly
C. pure competition
D. oligopoly
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The equilibrium quantity in a perfectly competitive market is determined:
A) at the point of intersection of the demand curve and the quantity axis. B) at the point of intersection of the demand and supply curves. C) at the point of intersection of the supply curve and the quantity axis. D) at the point of tangency between the demand and supply curves.
When there is a tendency for a particular product to fall out favor with additional consumers because other consumers have chosen not to purchase the product
A) negative market feedback occurs. B) positive market feedback occurs. C) the tit-for-tat strategy will begin. D) the network effect will increase.
Heuristic models are:
A. models expressed informally in words. B. highly mathematical models that are impossible to solve. C. based on scattergrams of two variables. D. models expressed informally by graphs.
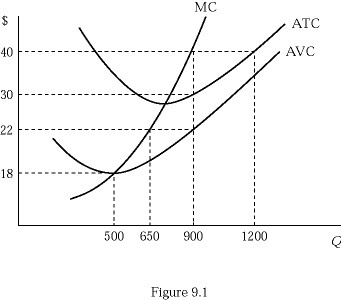 Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
A. $12,500. B. $14,300. C. $19,800. D. $27,000.