At a perfectly competitive equilibrium with production and trade, the slope of the production possibility curve will be
A) equal to the slope of the price line faced by the consumers.
B) steeper than the slope of the price line faced by consumers.
C) flatter than the slope of the price line faced by consumers.
D) either steeper or flatter than the price line faced by the consumers, depending upon the relative preferences of the consumers.
A
You might also like to view...
Explain how the economy moves back to full employment from recession. Be sure to detail what happens to short-run aggregate supply, unemployment, equilibrium GDP and the price level
What will be an ideal response?
China's recent economic performance is most similar to the experience of ________
A) the United States in the 1890s B) Japan in the 1960s & 1970s C) Cuba in the 1990s D) the Soviet Union in the 1950s & 1960s
If price is less than marginal cost, a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm should:
a. increase output. b. decrease output. c. decrease price. d. increase price.
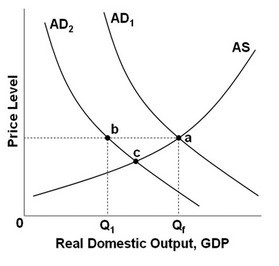 Refer to the above graph. The ratchet effect would suggest that:
Refer to the above graph. The ratchet effect would suggest that:
A. if AD1 moves to AD2, the new equilibrium would be at c. B. if AD2 moves to AD1, the new equilibrium would be at a. C. if AD1 moves to AD2, the new equilibrium would be at b. D. if AD2 moves to AD1, the new equilibrium would be at b.