Exhibit 6-2 Total utility for hamburgers, fries, and Cokes
Total Utilityfrom Hamburgers
Total Utilityfrom Fries
Total Utilityfrom Cokes
1 hamburger (100 utils)
1 order of fries (30 utils)
1 Coke (40 utils)
2 hamburgers (180 utils)
2 orders of fries (50 utils)
2 Cokes (60 utils)
3 hamburgers (240 utils)
3 orders of fries (60 utils)
3 Cokes (70 utils)
In Exhibit 6-2 assume that the price of hamburgers is $2 each, fries cost 50 cents each, and Cokes cost $1 each. What is the marginal utility of having a second order of fries?
A. 10 utils.
B. 20 utils.
C. 30 utils.
D. 50 utils.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
If the fluctuations in the economy's real growth rate from year to year are caused primarily by variations in the rate at which aggregate supply increases, then data would show
a. a cyclical relationship between inflation and unemployment. b. a direct relationship between inflation and unemployment. c. an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. d. no relationship between inflation and unemployment.
The output effect describes the situation when a monopolist sells more output and, all else equal, total revenue
a. increases. b. decreases. c. is unchanged. d. is maximized.
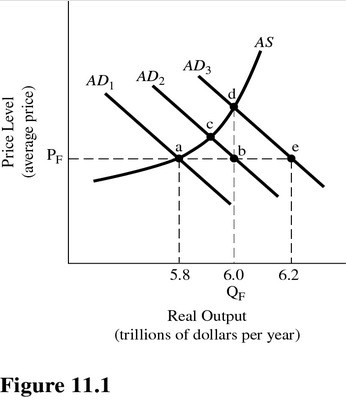 Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
A. $.2 trillion. B. $.6 trillion. C. $.4 trillion. D. None of the choices are correct.
Identify the correct statement.
A. The overall effects of the Uruguay Round on global pollution are actually small. B. The actual effects of the Uruguay Round on pollution levels are uniform across all countries. C. The composition effect of the Uruguay Round tends to increase production of environment-friendly products in the United States. D. Evidence shows that free trade is inherently anti-environment.