Measuring the national income accounts can NOT be helpful in explaining things like:
A. unemployment rates.
B. economic booms.
C. rates of inflation
D. rates of return on a firm’s capital.
D. rates of return on a firm’s capital.
You might also like to view...
Suppose that a borrower has a near-perfect credit history before the bank loans him some money. Shortly after the loan has been made, he loses his job and spends money recklessly. This describes the problem known as
A) moral hazard. B) adverse selection. C) risk aversion. D) asymmetric information.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. The Keynesian analysis assumes that ample resources will be available to increase production if planned investment increases when the economy is at less than full employment. 2. The Keynesian analysis differs from classical analysis in its short-run analysis of the economy. 3. The monetarist school is primarily concerned with unemployment and recessions. 4. The monetarist school is more similar to the Keynesian school than the classical school. 5. The time lags lead monetarists to contend that monetary policy is counterproductive. 6. The new classical school holds that rational expectations tend to defeat the goals of monetary policy. 7. The new classical school contends that government fiscal policy is better than monetary policy in controlling inflation.
Refer to the information provided in Table 8.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 8.6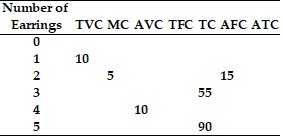 Refer to Table 8.6. From the information in the given table,
Refer to Table 8.6. From the information in the given table,
A. the marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve between 3 and 4 units of output. B. the firm is in the long run. C. the difference between total cost and total variable cost decreases as output increases. D. the firm eventually experiences diminishing returns to its variable input.
Assume the tennis ball industry, a perfectly competitive industry, is in long-run equilibrium with a market price of $5. If the demand for tennis balls increases and the industry experiences decreasing returns to scale, long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at a price
A. greater than $5. B. equal to $5. C. less than $5. D. either greater than or less than $5, depending on the number of firms that enter the industry.