Any risk-averse individual would always
A) take a 10% chance at $100 rather than a sure $10.
B) take a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at $1 rather than a sure $1.
C) take a sure $10 rather than a 10% chance at $100.
D) take a sure $1 rather than a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at losing $1.
E) do C or D above.
C
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph for a competitive market to answer the question below.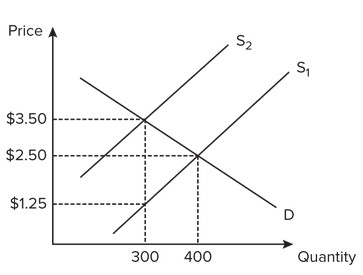 Assume the government imposes a $2.25 tax on suppliers, which results in a shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. The amount of the tax paid by the seller is
Assume the government imposes a $2.25 tax on suppliers, which results in a shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. The amount of the tax paid by the seller is
A. $2.25. B. $0. C. $1.00. D. $1.25.
The figure above shows how the PPF for cell phones and new cell-phone factories can expand. In the figure, if the economy produced 4 million cell phones using the resources efficiently, the PPF would
A) expand farther than shown in the figure. B) expand along the vertical axis and not along the horizontal axis. C) expand, but not as far as shown in the figure. D) expand evenly along both axes. E) not expand.
Which of the following can be categorized as a commodity money standard?
a. The pegged exchange rate standard b. The free float standard c. The managed float standard d. The reserve currency standard e. The gold standard
If a monopolistically competitive market is in long-run equilibrium, each firm
A. earns economic profits. B. charges a price which is higher than long-run marginal cost. C. produces that level of output at which long-run average cost is minimum. D. all of the above E. none of the above