Why has the use of the FCAW process increased for pipe??
What will be an ideal response?
Improvements in welding equipment and manufacturing techniques for producing flux cored wire and a wider array of filler metal and flux alloys have increased the use of FCAW for pipe.?
You might also like to view...
When it comes to communication, what do we consider a worst-case scenario?
What will be an ideal response?
How far is T.L. 0'- 0" from the base of the skirt?
Refer to Drawing Numbers E492877 R0 and E482878 R0.
Which of the following statements is accurate?
An ammonia synthesis process works as follows: Fresh feed air and hydrogen are combined with a recycle stream and the combined stream is compressed to 10 MPa. The compressed stream enters a reactor, and a fraction of the entering nitrogen and hydrogen are converted into ammonia. The reactor effluent, still at 10 MPa, enters a condenser. The liquid and vapor streams leaving the condenser are in VLE. The liquid stream, which is almost pure ammonia, is the product. A fraction of the vapor stream leaving the condenser is purged, while the rest is recycled. A. Raoult’s Law would be a reasonable way to model the VLE for ammonia in the condenser. B. Henry’s Law would be a reasonable way to model the VLE for oxygen in the condenser. C. If we increase the size of the reactor, allowing a larger fraction of the nitrogen and hydrogen to be converted to ammonia, it won’t lead to an increase in the liquid product flow rate, because the product flow rate is limited by the equilibrium constraint in the condenser. D. If we maintain the same flow rate of entering feeds, but we purge a smaller fraction of the vapor leaving the condenser, then the mole fraction of oxygen in the purge stream will go down. E. None of the above are true.
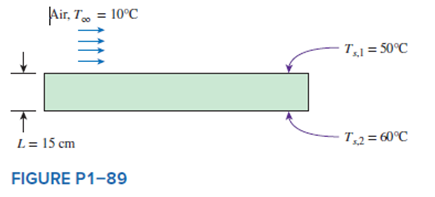
A solid plate, with a thickness of 15 cm and a thermal conductivity of 80?W/m•K, is being cooled at the upper surface by air. The air temperature is 10°C, while the temperatures at the upper and lower surfaces of the plate are 50 and 60°C, respectively. Determine the convection heat transfer coefficient of air at the upper surface, and discuss whether the value is reasonable or not for forced convection of air.