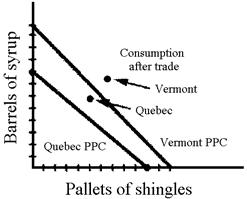
Quebec is capable of producing 10,000 pallets of wood shingles or 8,000 barrels of maple syrup. Vermont is capable of producing 12,000 pallets of wood shingles or 12,000 barrels of maple syrup.
a. Graph these production possibilities curves. Indicate from the slope, which has the absolute advantage, which the comparative advantage, and whether there are gains from trade.
b. Assume that Vermont and Quebec each specializes in the good in which they have a comparative advantage. Suppose that Vermont and Quebec decide to trade 5,000 pallets of shingles for 5,000 barrels of syrup. Indicate this on the graph. How does this affect the well-being of the two societies? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
?
?
a. See Figure 34-11. Quebec has a comparative advantage in the production of shingles, although Vermont has an absolute advantage. Vermont has a comparative advantage in the production of syrup as well as the absolute advantage. Both Quebec and Vermont can gain (i.e., be better off in terms of consumption of shingles and syrup) if they specialize where they have a comparative advantage, and trade for the other good.
b. The consumption points are shown on the graph. Quebec now consumes a combination of goods above its production possibilities curve, and has gained from trade. Vermont consumes at a point on its production possibilities curve, and has not gained from trade. While unusual, this case cannot be ruled out from trade theory.
You might also like to view...
Shaniq can spend the next hour studying for a finance test, hiking along the Oregon coast, watching reruns of Lost on television, or napping
If she decides to study, what is the opportunity cost of her choice: hiking, watching television, or napping?
Profit-related income does not play any crucial role in the workings of a market system
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Contractionary monetary policy, achieved by selling bonds in the open market, tends to discourage investment.
a. true b. false
In the United States, trade adjustment assistance
A. is often criticized on the ground that it provides benefits to millions of workers each year who have not actually been affected by increased imports. B. provides incentives for workers to search for new jobs outside an import-competing industry before they lose their jobs in this industry. C. provides subsidies to firms who produce exportable commodities. D. provides workers who have been displaced from import-competing firms with additional months of unemployment compensation.