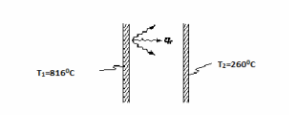
Two large parallel plates with surface conditions approximating those of a blackbody are maintained at 816 and 260°C, respectively. Determine the rate of heat transfer by radiation between the plates in W/m2 and the radiative heat transfer coefficient in W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• Two large parallel plates, approximately black bodies
• Temperatures
? T1 = 816°C = 1089 K
? T2 = 260°C= 533 K FIND
(a) Rate of radiative heat transfer (qr/A) in W/m2 (b) Radiative heat transfer coefficient (hr) in W/(m2 K) ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state prevails
• Edge effects are negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Stefan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 ? 10–8 W/(m2 K)
(a) The rate of heat transfer is given
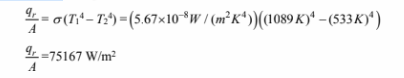
(b) Let hr represent the radiative heat transfer coefficient
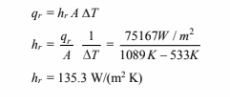
You might also like to view...
In the normal eye the ciliary muscles that control the lens will relax
a. when viewing objects at the near point. b. when viewing objects at infinity. c. when viewing objects at a distance of 20 ft. d. only when a person has his/her eyes closed.
A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave in vacuum delivers energy at an average rate of 5.00 µW/m2
What are the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields of this wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, ?0 = 4? × 10-7 T ? m/A, ?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ? m2)
Oxygen molecules are 16 times more massive than hydrogen molecules. At a given temperature, the average molecular kinetic energy of oxygen molecules, compared to that of hydrogen molecules,
A) is greater. B) is less. C) is the same. D) cannot be determined without knowing the pressure and volume.
What kind of lens is it that has a power of +10 Diopters and a first surface center of curvature in front of the lens?
A) double convex B) double concave C) converging meniscus D) plano concave E) plano convex