If a natural monopolist were to sell at the price where marginal cost equals demand, then it would be earning
a. zero economic profits, like a competitive firm in the long-run.
b. negative profits and would not be able to survive.
c. positive profits but not would not need to worry about government intervention to regulate it.
d. positive profits but would still need to worry about possible government intervention to regulate it.
b. negative profits and would not be able to survive.
You might also like to view...
Suppose the shift from AD0 to AD1 and from AS0 to AS1 is the result of fiscal policy. Which of the policies below could lead to these shifts?
i. An increase in government expenditure ii. A tax cut iii. A decrease in government expenditure iv. A tax hike A) iv only B) i and ii C) i and iv D) i only E) iii and iv
As we move downward along a demand curve for apples,
A) consumer well-being decreases. B) the marginal utility of apples decreases. C) the marginal utility of apples increases. D) Both A and B are true. E) Both A and C are true.
This graph represents the cost and revenue curves of a firm in a perfectly competitive market.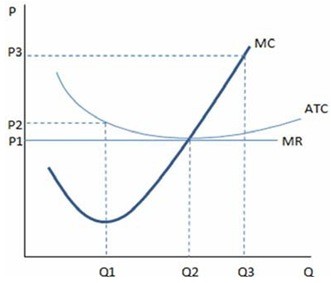 According to the graph shown, if a firm is producing at Q1:
According to the graph shown, if a firm is producing at Q1:
A. the firm should not increase production because it will earn loss. B. average total costs exceed the market price. C. marginal revenue is greater than average total cost. D. profits are being maximized.
What are the Euler Equations?
A. another name for the objective function B. another game for the first order conditions, defining optimal choices C. equations relating the optimal choice of interest rates to other prices D. both A and B, but not C