As discussed in the Case in Point on the size of the fiscal multiplier, a study conducted by John Taylor on the effect of fiscal policy since the year 2000 suggests that
A) the multiplier effect of fiscal policy is much less than that for monetary policy.
B) temporary fiscal policy financed through government borrowing implies a multiplier value between 0.8 and 1.5.
C) fiscal policy has little effect on the economy and that the multiplier value is effectively zero.
D) statistical models are inadequate to determine the multiplier and the multiplier value likely varies based on the state of the economy.
Ans: C) fiscal policy has little effect on the economy and that the multiplier value is effectively zero.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 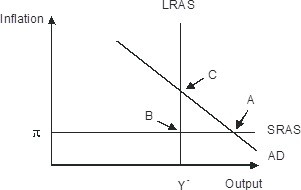
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, most U.S. adults are either
A) employed or unemployed. B) employed or not in the labor force. C) unemployed or not in the labor force. D) unemployed or underemployed.
What are two arguments against using the economic method?
a. It is not a fair and diverse approach. b. It is not possible to prove that people behave rationally. c. People do not and should not take only economic factors into their decision making. d. It is too complicated and theoretical.
The basic difference between macroeconomics and microeconomics is that:
a. microeconomics looks at the forest (aggregate markets) while macroeconomics looks at the trees (individual markets). b. macroeconomics is concerned with groups of individuals while microeconomics is concerned with single countries. c. microeconomics is concerned with the trees (individual markets) while macroeconomics is concerned with the forest (aggregate markets). d. macroeconomics is concerned with generalization while microeconomics is concerned with specialization.