List the three types of website structures, and give an example of how each might be used.
What will be an ideal response?
Alinear/tutorial website structureorganizes and presents webpages in a specific order. A training website could use this structure to ensure that users do not miss steps or perform steps out of sequence. The linear/tutorial structure controls the navigation of users by progressing them from one webpage to the next. This structure is also appropriate for information presented in a historical or chronological order; for example, a website that details the explosive growth of e-commerce might benefit from this structure.?Awebbed website structure, also called arandom website structure, does not arrange its pages in a specific order. From the home page of a website organized around a webbed structure, visitors can choose any other webpage according to their interests or inclinations. Websites that use a webbed structure need to provide a search feature so that website visitors easily can find the information they need. Webbed structures work well for some informational websites, catalogs, and other websites that use search features or dynamic content. Ahierarchical website structureorganizes webpages into categories and subcategories by an increasing level of detail. Organizational and topical websites usually are well suited to a hierarchical structure. A university website, for example, might structure its webpages in three categories with multiple subcategories:?• Academics category with departments and majors subcategories• Athletics category with teams and schedules subcategories• Students category with current and prospective students and alumni subcategories
You might also like to view...
Consider a particle with mass m. As its speed approaches the speed of light, its relativistic momentum magnitude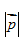 approaches:
approaches:
A. infinity B. mc C. m D. zero
The wavelength of maximum intensity is useful in measuring the ____
a. surface temperatures of an object from their colors b. distance to an object from their colors c. chemical composition of an object d. motion of an object across the observer's line of sight e. motion of an object toward or away from the observer
What happens when a particle of matter meets its corresponding antiparticle of antimatter?
A) They can form a complete atom. B) The combined mass of the two particles is completely transformed into energy (photons). C) They fuse to make a heavier particle. D) The question makes no sense, since antimatter does not really exist.
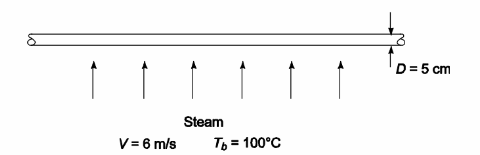
Steam at 1 atm and 100°C is flowing across a 5-cm-OD tube at a velocity of 6 m/s. Estimate the Nusselt number, the heat transfer coefficient, and the rate of heat transfer per meter length of pipe if the pipe is at 200°C.
GIVEN
• Steam flowing across a tube
• Steam pressure = 1 atm
• Steam bulk temperature (Tb) = 100°C
• Tube outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
• Steam velocity (V) = 6 m/s
• Pipe surface temperature (Ts) 200°C
FIND
(a) The Nusselt number Nu D (b) The heat transfer coefficient h c(c) The rate of heat transfer per unit length (q/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0249 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 20.2 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.987 At the tube surface temperature of 200°C, the Prandtl number of the steam (Prs) = 1.00