What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
What will be an ideal response?
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the more of any one good consumed in a given period the less satisfaction generated by consuming each additional unit of the good.
You might also like to view...
The table above shows the marginal costs and marginal benefits of college education. With public provision of the efficient amount of college education, the cost paid by the taxpayers is
A) zero. B) $8,000 per student. C) $4,000 per student. D) $12,000 per student.
The person on the other side of a transaction is referred to as the:
A) derivator B) counterparty C) hedger D) speculator
When the demand for a monopolist's output falls, the monopolist will
a. not change the price, since it has no competition. b. raise the price in order to compensate for the lower demand. c. charge a lower price. d. cut its costs in order to maintain its profit margin.
Refer to the figures below to answer this question:
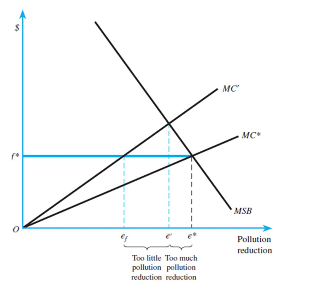
Cap-and-trade versus emissions fee when marginal social benefits are inelastic and costs are
uncertain:
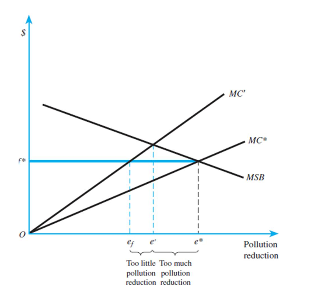
Cap-and-trade versus emissions fee when marginal social benefits are elastic and costs are uncertain:
a) In case of an inelastic marginal social benefit curve, what type of pollution reduction system should the government employ? Why?
b) If the social benefit curve is elastic, do you answer change?
c) What are advantages and disadvantages of Cap-and-Trade systems over Emission Fee
systems when the inflation and change in marginal costs are considered?