The force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field is the strongest when
A)
the current is parallel to the field lines.
B)
the current is at a 30° angle with respect to the field lines.
C)
the current is at a 45° angle with respect to the field lines.
D)
the current is at a 60° angle with respect to the field lines.
E)
the current is perpendicular to the field lines.
E
You might also like to view...
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity v2 = 2.1 m/s at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C?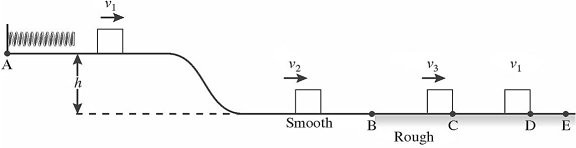
style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="148" width="576" /> A. -1.8 J B. -3.6 J C. -14 J D. -6.4 J E. -7.0 J
When you interchange your emitter for one with a smaller work function, you measure
Sand dunes form as wind
A) disperses sand. B) blows sand from the back to the front of the dune. C) blows sand from the front to the back of the dune. D) interrupts the normal sequence of deposition.
A bomb blast sends a shock wave through the 20°C atmosphere. At a certain location, the shock wave is travelling at M = 3. The induced velocity behind the wave is nearest:
(A) 760 m/s (B) 620 m/s (C) 540 m/s (D) 410 m/s