If the exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and the American dollar was fixed at 1.30 Canadian dollars per U.S. dollar and investors perceived Canadian bonds to be equal in value and risk to U.S. bonds, if the U.S. bonds are selling for $1,000 and have a 5 percent interest rate, assuming capital flows freely between the two countries what will be the price and the interest rate of the Canadian bonds?
What will be an ideal response?
The price of the Canadian bonds will be 1,300 Canadian dollars or 1,000 U.S. $s and the interest rate on the Canadian bonds will also be 5%. This comes from the equation: $1,000(1 + i) = $1,000(1 + if).
You might also like to view...
Open-market operations, changes in reserve requirements, changes in the discount rate, and changes in the interest rate on reserves are known as
A) goals. B) intermediate targets. C) instruments. D) derivatives.
A monopolist is a price maker
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The economic boom of the early 1940s resulted mostly from
a. increased government expenditures. b. falling prices of oil and other natural resources. c. an increase in the growth rate of the money supply. d. rapid developments in transportation, electronics, and communication.
Refer to the accompanying figure. The opportunity cost of producing one bushel of corn is: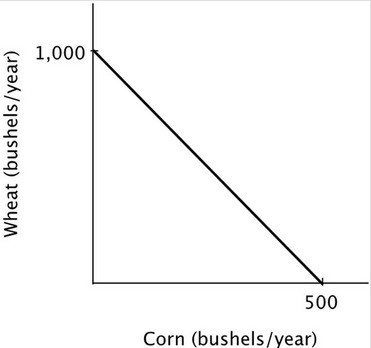
A. 250 bushels of wheat. B. ½ of a bushel of wheat. C. 500 bushels of wheat. D. 2 bushels of wheat.